Overview

Striker
This style may not reveal (strike to) its target color until fired.
Reactive Potential
Contains: Sulfur (S) / Selenium (Se)
May React With: Copper (Cu), Lead (Pb), and Silver (Ag)
Forms of Glass
Sheet Glass (-0030, -0050), Frit (-0001, -0002, -0003, -0008), Rod (-0576) and Stringer (-0272, -0107)
Detailed Information
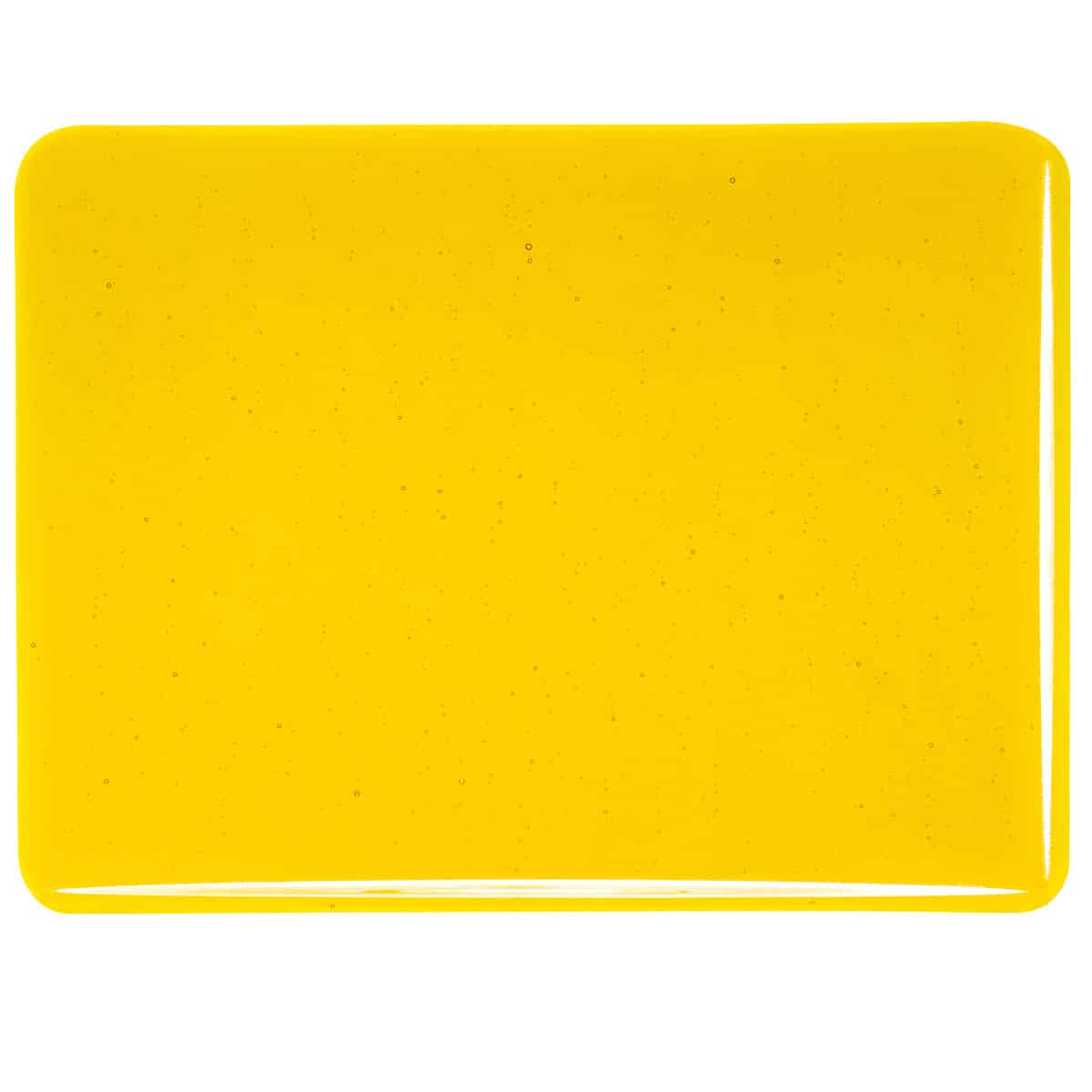
About 001120 Sheet Glass
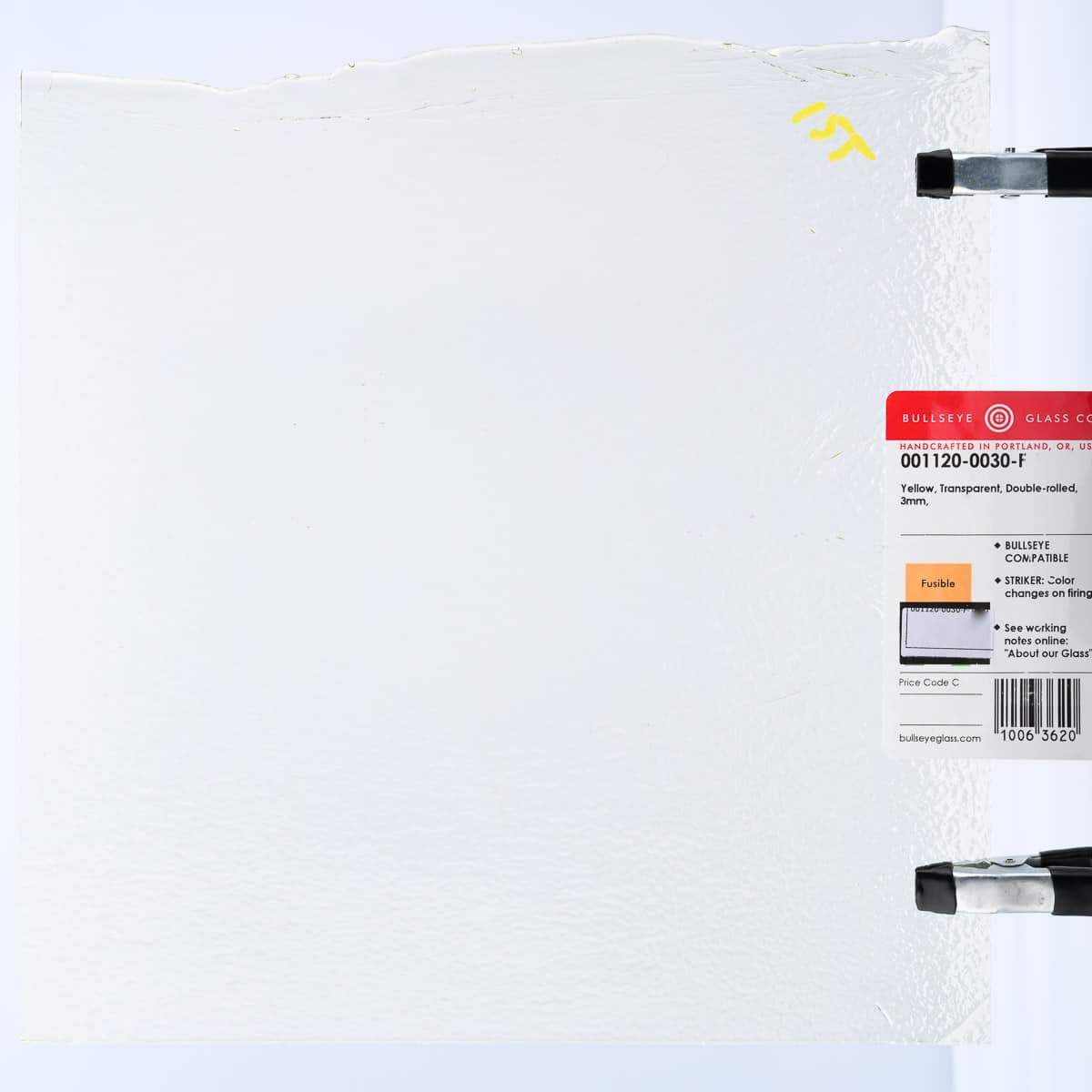

Cold Characteristics
Consistent color.

Working Notes
A cadmium glass.
This style is not suitable for kilncasting because it can opalize and/or become incompatible when held at high temperatures for an extended period. It may also opalize and/or become incompatible in instances where processes exceed the parameters of the test for compatibility. Testing recommended when heatwork exceeds these parameters.
About 001120 Frit
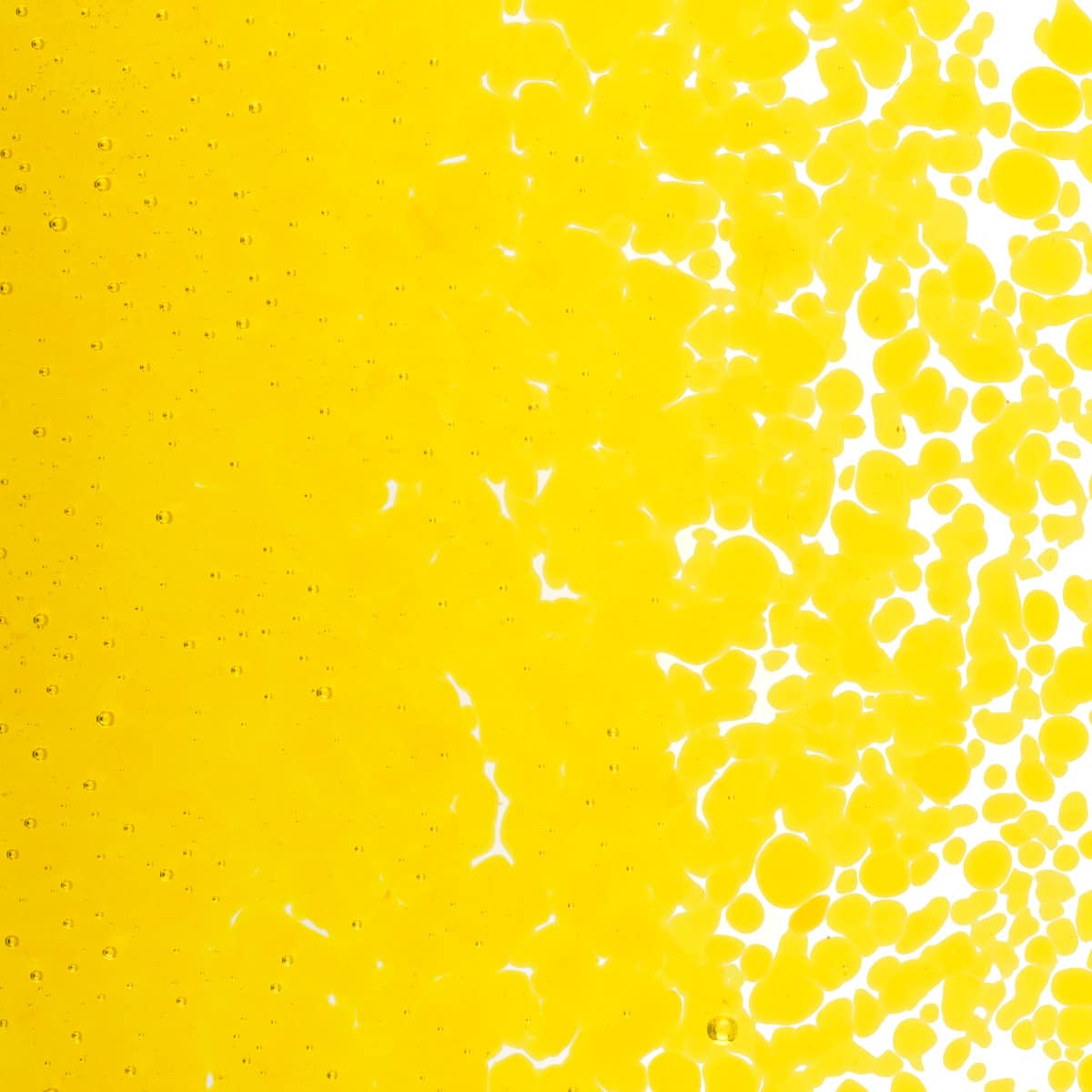
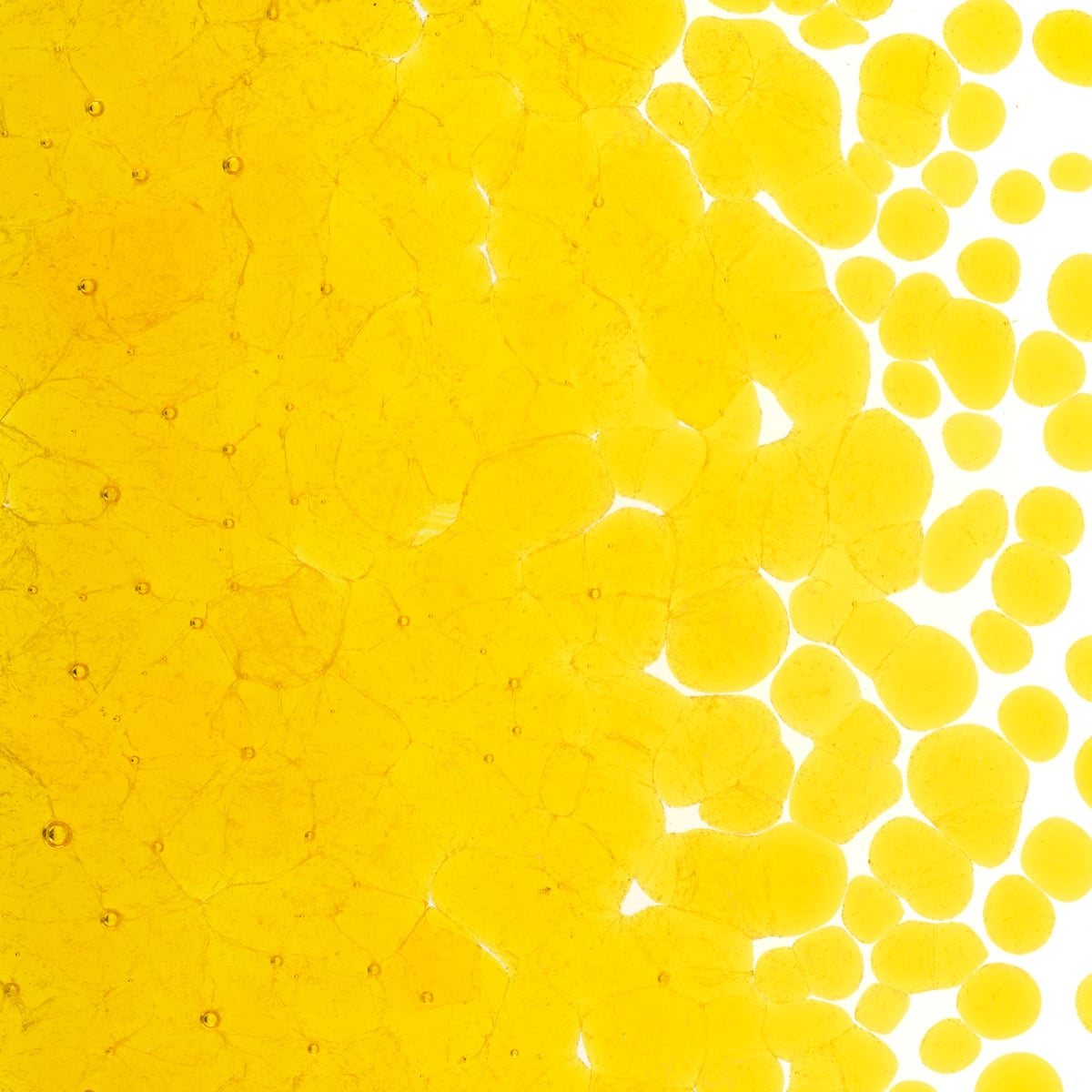
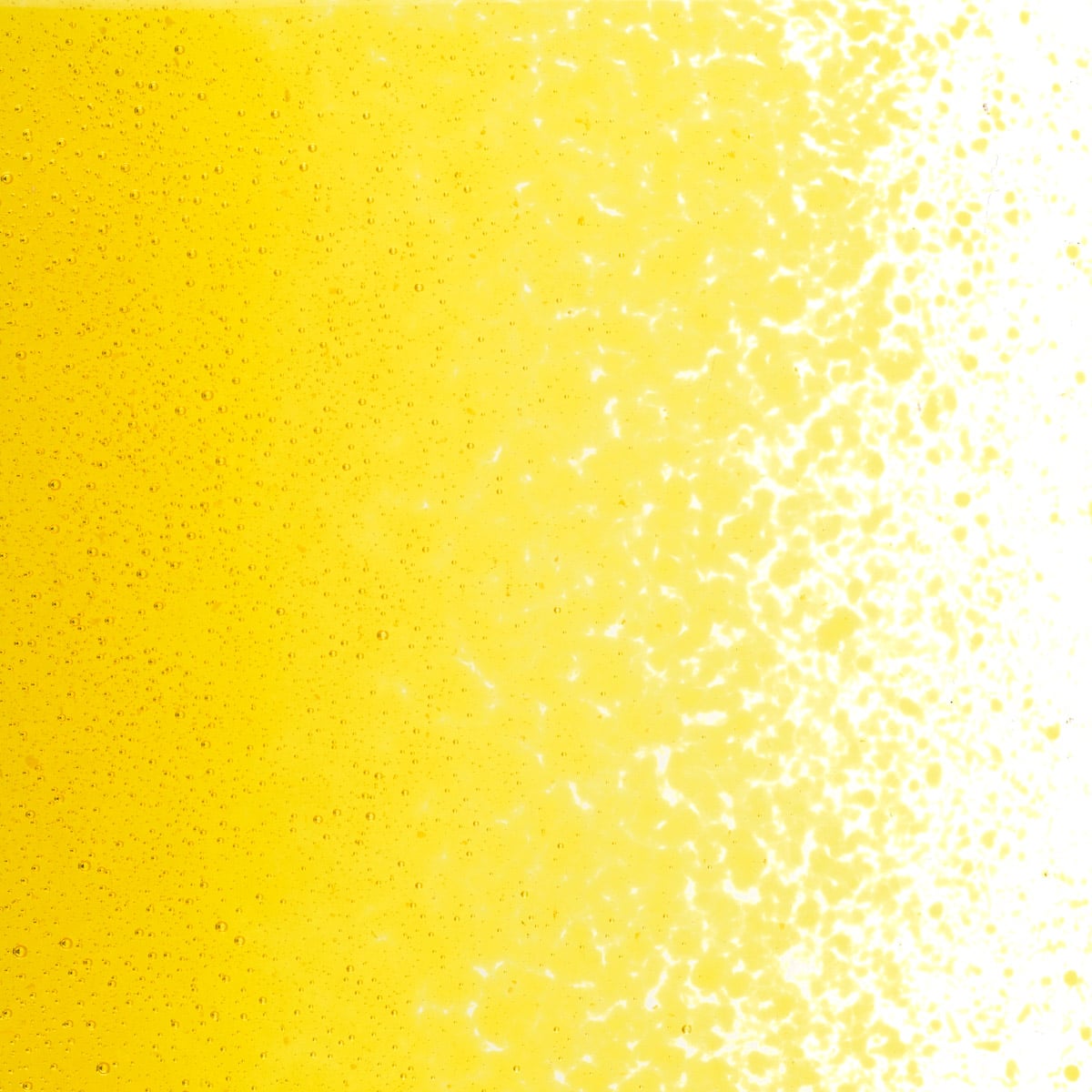




Working Notes
This style is not suitable for kilncasting because it can become incompatible when held at high temperatures for an extended period. It may also become incompatible in instances where processes exceed the parameters of the test for compatibility. Testing recommended when heatwork exceeds these parameters.
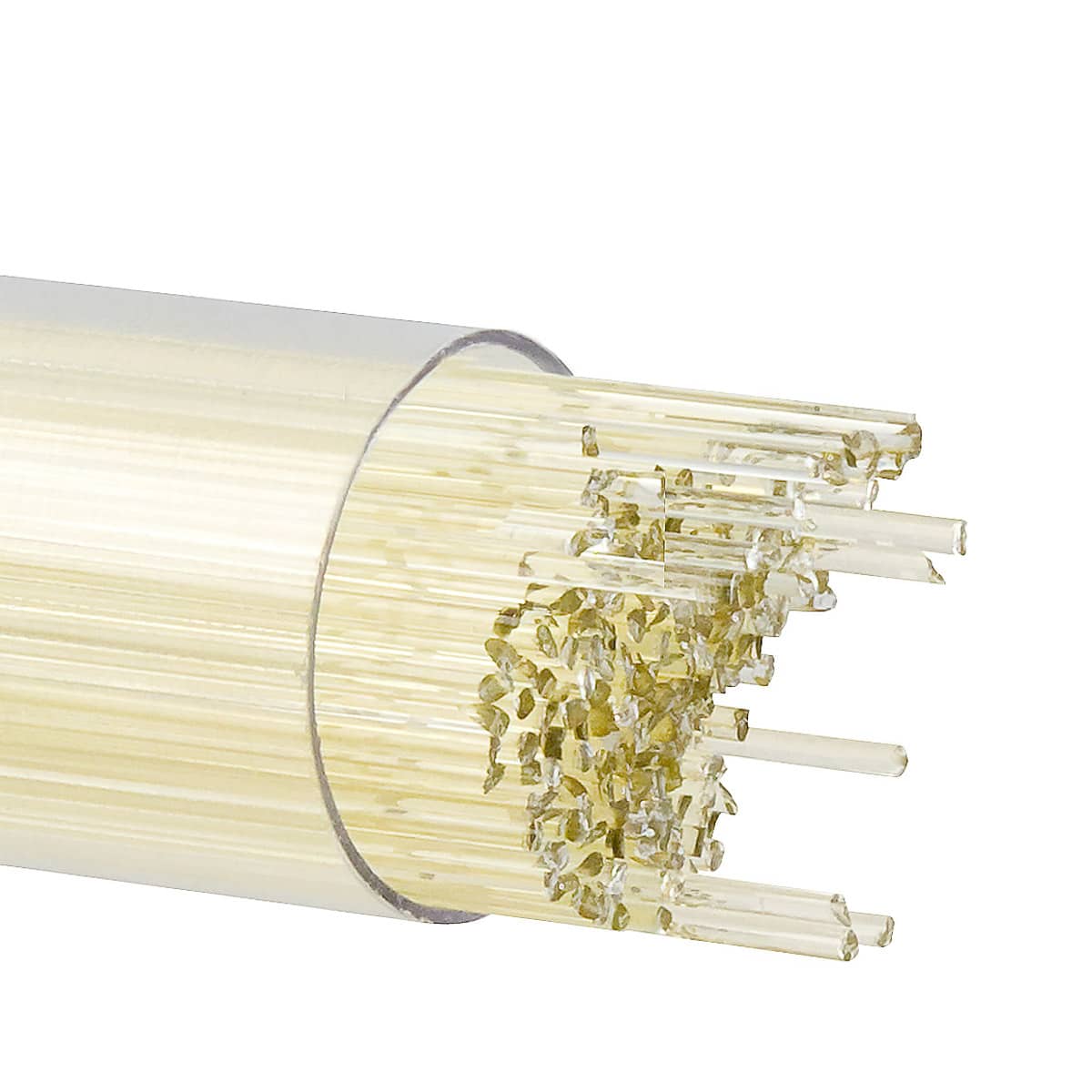
About 001120 Rod
Cold Characteristics
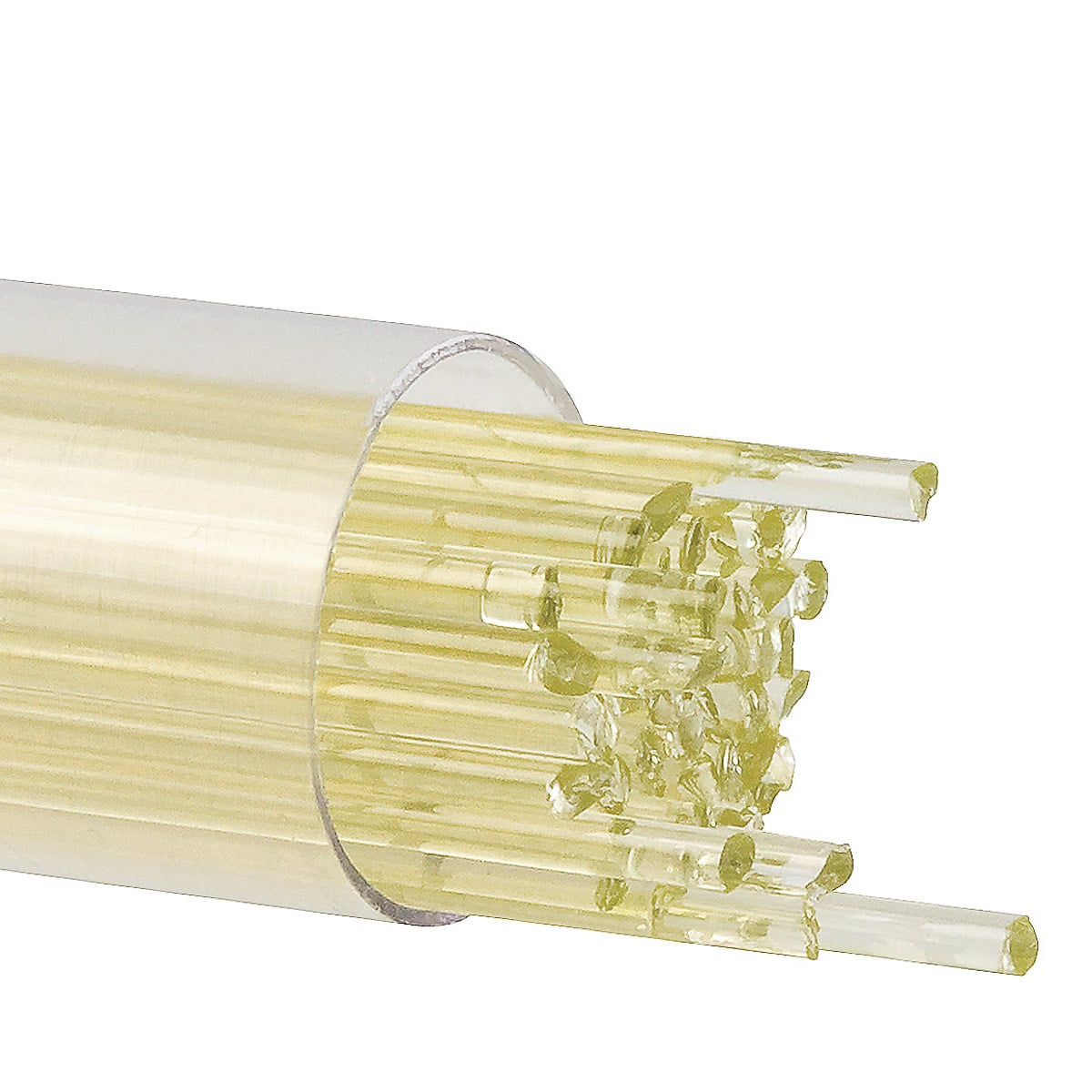
Pale transparent amber, similar to Orange Transparent Rod (001125-0576) and Light Amber Transparent Rod (001437-0576). May have a struck streak of yellow running lengthwise down the rod.
Working Notes
Torch: Yellow color develops in the flame. Keep 001120-0576 transparent by using it in small amounts with minimal heatwork, or consider adding it towards the end of the time in the flame. We advise labeling all striking glasses.
Kiln: This style is not suitable for kilncasting because it can become incompatible when held at high temperatures for an extended period. It may also become incompatible in instances where processes exceed the parameters of the test for compatibility. Testing recommended when heatwork exceeds these parameters.
About 001120 Stringer
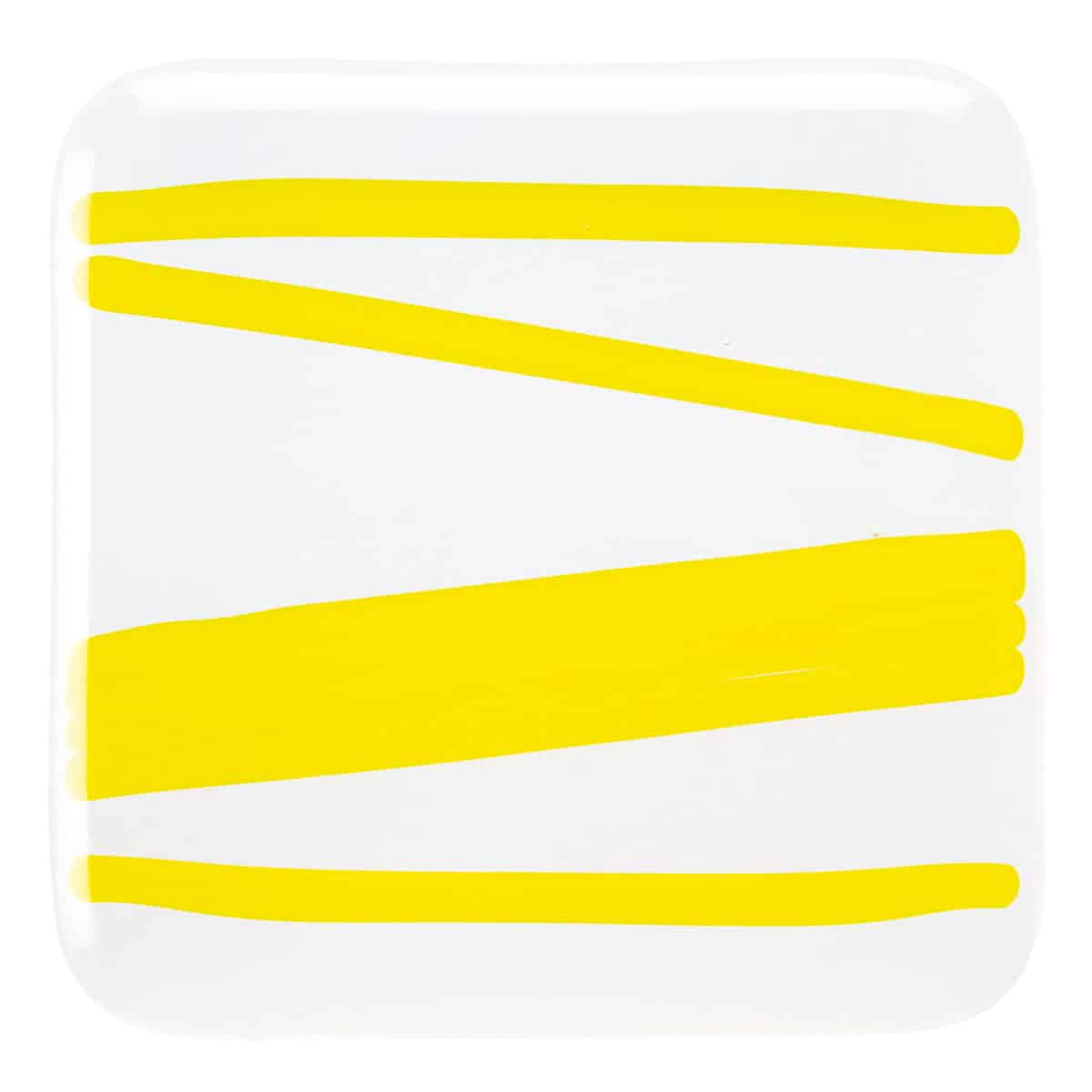
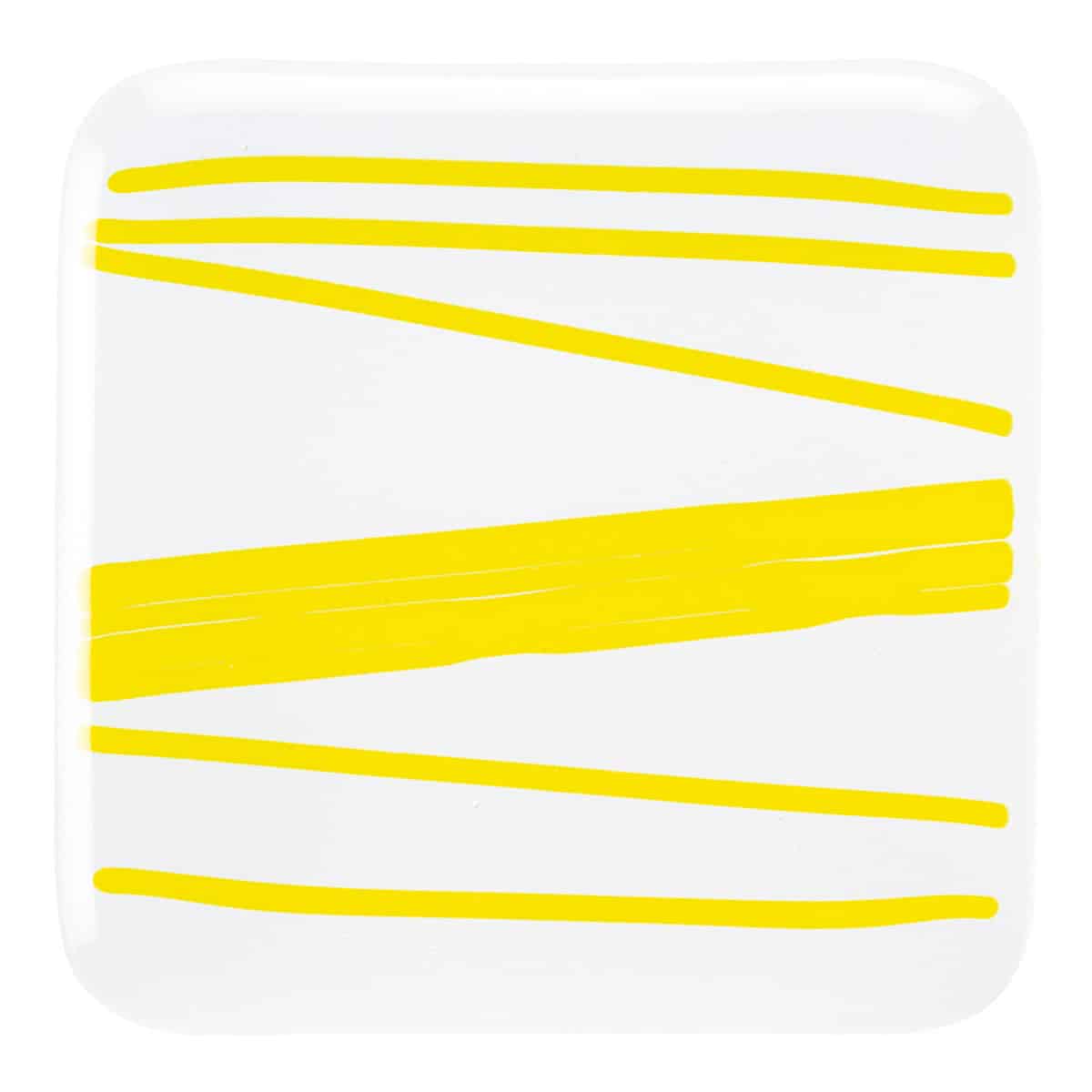



Working Notes
This style is not suitable for kilncasting because it can become incompatible when held at high temperatures for an extended period. It may also become incompatible in instances where processes exceed the parameters of the test for compatibility. Testing recommended when heatwork exceeds these parameters.
